Resources
Understanding Charts and Chart Patterns
Posted on Aug. 18, 2024, 3:30 p.m.
Author: Merlo Ovie
Introduction to Charts
Charts are essential tools for traders and investors, providing a visual representation of price movements over time. They help in identifying trends, making predictions, and spotting potential trading opportunities. The most common types of charts are line charts, bar charts, and candlestick charts.
Types of Charts
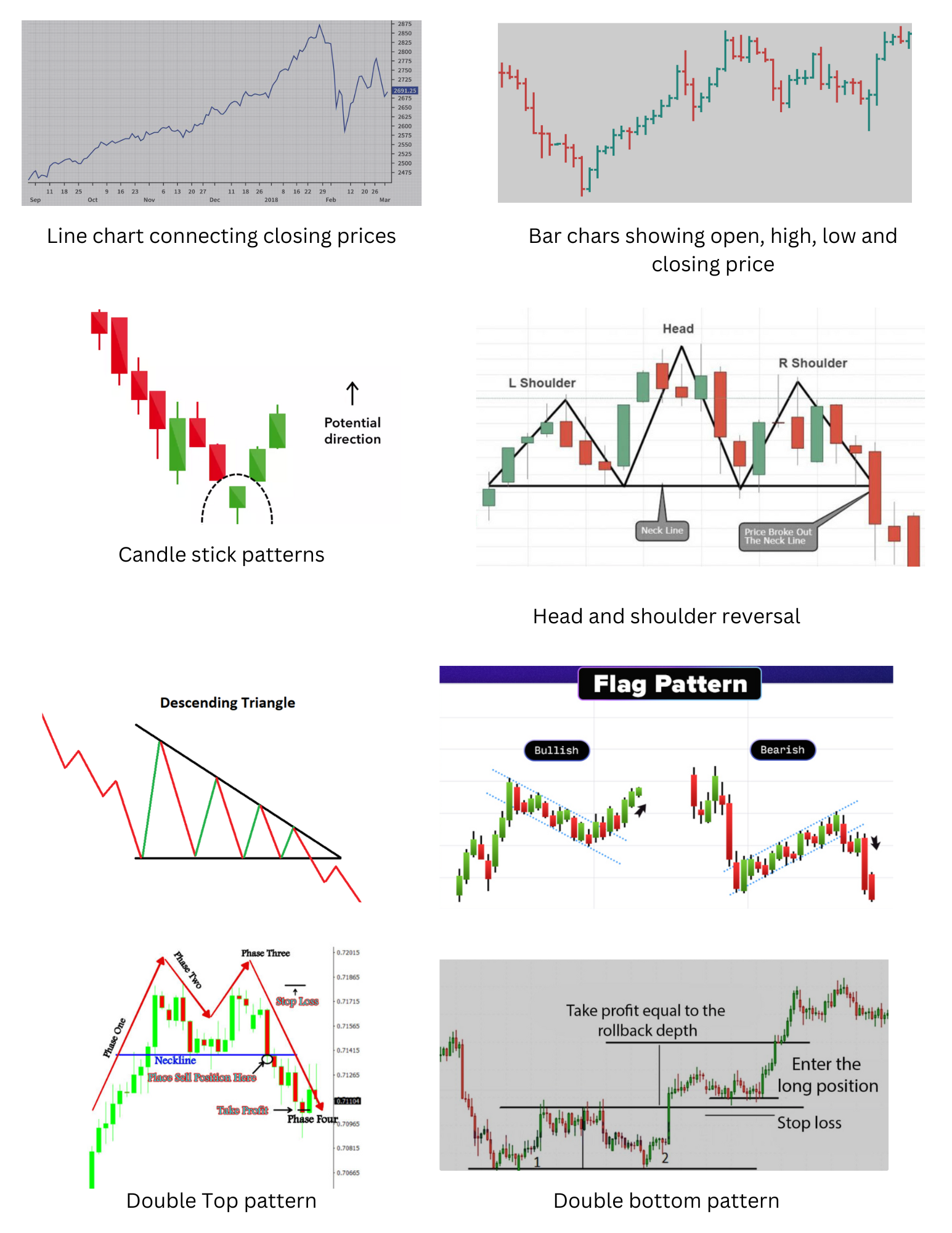
1. Line Chart:
Description: A simple chart that connects closing prices over a set time period with a line.
Use: Best for observing overall price trends and patterns.
2. Bar Chart:
Description: Displays the high, low, opening, and closing prices for a specific time period, forming a vertical bar.
Use: Useful for identifying price ranges and trends within a specific period.
3. Candlestick Chart:
Description: Similar to a bar chart but uses 'candlesticks' to show the open, close, high, and low prices. The body shows the difference between the open and close, while the wicks indicate the high and low.
Use: Popular for spotting market sentiment and predicting potential reversals.
Understanding Chart Patterns
Chart patterns are shapes or formations on a chart that indicate potential future price movements. They are broadly categorized into continuation and reversal patterns.
1. Continuation Patterns
Description: These patterns suggest that the current trend will continue after a brief consolidation.
Common Patterns:
Triangles (Ascending, Descending, Symmetrical): Represent a battle between buyers and sellers, often leading to a breakout in the direction of the existing trend.
Flags and Pennants: Short-term consolidation patterns that typically lead to a continuation of the trend.
2. Reversal Patterns
Description: These patterns signal that the current trend is likely to reverse.
Common Patterns:
Head and Shoulders: A pattern indicating a bullish-to-bearish reversal (or vice versa in an inverse head and shoulders).
Double Tops and Double Bottoms: Indicate a reversal after failing to break a price level twice.
Cup and Handle: A bullish continuation pattern where the price forms a 'U' shape followed by a small consolidation, resembling a handle.
Conclusion
Charts and chart-patterns are critical for understanding market behavior and predicting future price movements. By mastering these tools, traders can make more informed decisions and improve their trading outcomes. However, it's important to combine chart analysis with other forms of research and analysis for the best results.
Overview of Forex Trade
Posted on Aug. 18, 2024, 4:12 a.m.
Author: Merlo Ovie
The basic trading principle is to buy and sell assets to make a profit. These assets can include stocks, bonds, commodities, and currencies in the case of Forex trading. Trading involves assessing risks and opportunities associated with these assets and making informed decisions based on market conditions, trends, and other financial instruments.
Understanding Forex Trading
While trading stocks involves buying and selling company ownership, Forex trading (foreign exchange trading) is about trading one currency for another. The Forex market is the world's largest and most liquid financial market, operating 24 hours a day, five days a week. In this market, currencies are traded in pairs, such as EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar) or GBP/JPY (British Pound/Japanese Yen). When you trade Forex, you're betting on whether one currency will strengthen or weaken against another.
How Forex Differs from Stock Trading
In stock trading, you buy shares hoping that the company will perform well, increasing the value of those shares, which you can then sell at a higher price. In Forex trading, the goal is similar but involves predicting the movement of currency exchange rates. For example, if you believe the Euro will strengthen against the US Dollar, you will buy Euros with Dollars. If the Euro’s value increases relative to the Dollar, you can sell the Euros for a profit.
The Role of Psychology in Trading
Like in stock trading, psychology plays a significant role in Forex trading. Market sentiment, driven by traders' collective psychology, can cause rapid fluctuations in currency prices. Fear, greed, and other emotions can lead to impulsive decisions, making trading more challenging than it appears. Successful traders often focus on managing their emotions, sticking to their strategies, and avoiding the pitfalls of chasing profits or panicking during market downturns.
Conclusion
In both stock and Forex trading, the key to success lies in understanding the assets you are trading, assessing the risks, and managing your emotions. Whether you’re dealing with shares of a company or currency pairs, the fundamental principle remains the same: buy low, sell high. However, it's important to remember that making informed decisions based on market analysis is more reliable than trading based on emotion.
